
21 Essentials For An Enterprise SEO Audit
In this step-by-step guide, we’ll be exploring how to complete enterprise SEO audits for large B2B sites. We’ll discover how these website audits differ from those for small sites, which tools you need, and the technical and content SEO strategies that give you the best return from your efforts.
When dealing with large sites, the sheer number of pages can be overwhelming. You can’t simply take a page-by-page approach but need to prioritise different SEO factors to maximise the return on investment.
At the end of this guide, you will have created an enterprise SEO audit that delivers actionable results given the limited resources available for implementing change.
Why is an SEO audit important for large sites?
The larger the site, the more likely it is that you are missing out on valuable opportunities to increase organic traffic. Conducting an enterprise SEO audit allows you to identify easy fixes that will boost the ranking of the whole site. These low-hanging fruit might be in the form of default metatag structure, page speed factors affecting multiple web pages, or other technical SEO factors.
With an enterprise SEO audit, you can refine your digital marketing strategy based on your top-ranking competitors. You can also identify your own top-ranking pages and what it is that makes them stand out.
A website audit is not just about identifying SEO mistakes. It’s also about identifying opportunities to stand out from the crowd and reach that treasured first position.
To succeed, you have to take into account a myriad of interacting factors, as shown below.

SEO tools
You need a range of SEO tools to complete an audit and we have recommended free SEO tools whenever possible. The tools are:
- Google Analytics 4
- Search Console
- Screaming Frog
- Web Developer (Chrome Addon)
- Semrush or Clearscope for semantic keyword research
- Semrush or Ahrefs for backlink audits
If you don’t already have them installed, see how to set up your Google Analytics 4 account and Search Console account.
Identify your key performance indicators
1. Overall goals
Before starting your audit, it’s useful to identify your Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). What are you trying to achieve and which particular aspects of site performance are you looking to enhance?
Consider:
- Which business areas you want to expand in.
- Anticipated increase in sales or profits from different sectors.
- Current traffic. This can be measured using Clicks in Google Search Console or traffic estimates from Semrush or Ahrefs.
- Potential traffic change. Measured based on Impressions in Search Console or traffic volumes from Semrush or Ahrefs.
2. Target landing pages
Part of the KPIs will include identifying priority landing pages. This can be done in several ways:
- Current traffic.
- Potential traffic from target keywords.
- Positions for specific keywords.
- Conversions as measured by Google Analytics.
We recommend using a range of KPI’s – some for your site as a whole, others for specific landing pages or keywords. Start by providing data on your current rankings, clicks, traffic, etc. in order to demonstrate the success of your SEO audit.
3. Keyword research
For each landing page, do keyword research and identify one or more keywords per URL. For enterprise SEO it’s likely your priority pages will already receive significant traffic. Search Console is therefore an ideal free tool for this:
- Open Search Console
- Click Search Results
- Click Average position
- In the top menu, click New Page, then change the setting to ‘Exact URL‘ and enter the URL you wish to do keyword research for.
- Target keywords that are relevant, likely to convert and have high Clicks and good Positions.
Repeat the last 2 steps for each of your priority web pages.
Technical enterprise SEO audit
Technical SEO encompasses elements that prevent Google from indexing your site and factors that affect multiple web pages simultaneously. To ensure your site appears in Google’s index, conducting a technical SEO audit is paramount. Technical SEO serves as the foundation for your whole site.
4. 4xx errors
A 200 status code means a page loaded successfully. 4xx status codes means there was an error when the page was accessed. Some of the more common errors include:
- 401 Unauthorised
- 403 Access Forbidden
- 404 Page Not Found
To scan your site for 404 and other errors:
- Install Screaming Frog, a free SEO audit tool.
- Select Mode, Spider
- Enter your domain name
- Click Response Codes
- From the drop-down list, filter it by Client Error (4xx)
- Choose Internal
- Press Export
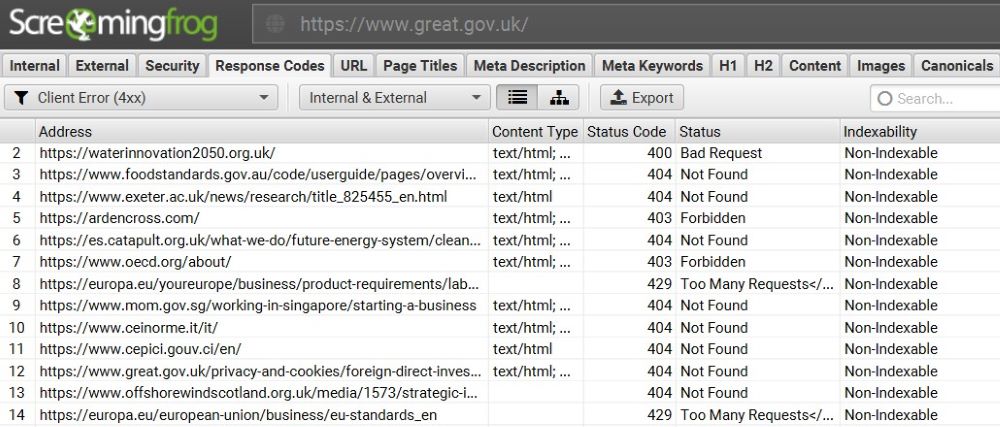
This will generate a spreadsheet showing all the pages with errors. For large websites with more than 500 pages, you will need the paid version of Screaming Frog.
You can also view the Page Indexing Report in Google Search Console, which shows which pages are in Google’s index and summarises why pages aren’t indexed.
5. Broken links
The easiest way to fix internal broken links is to 301 redirect 404 errors to the correct page. If all your internal pages are redirected to an appropriate page, this fixes all your internal broken links too.
To fix external broken links (those going to third-party websites), repeat the above steps, then:
- Choose External instead of Internal
- Click any of the errors
- Press Ctrl + A to select all of them
- In the footer menu of Screaming Frog, select Inlinks
- Press Export

This then exports a spreadsheet showing both the external 404 pages and the internal page linking to them. For each external error, either:
- Find an alternative external resource to link to.
- Internally link to a relevant page.
- Remove the hyperlink and edit the text around it as necessary.
6. Page speed (from March 2024, ‘Interaction to Next Paint’ will be introduced)
It’s always useful to anticipate upcoming Google algorithm changes in your website audit. From March 2024, Google will be replacing current page speed metrics with Interaction to Next Paint (INP).
To access their new page loading report:
- Open Search Console
- Click Core Web Vitals
- Click INP issues table in the paragraph below:
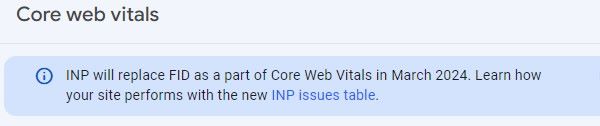
This then tells you how your site ranks on Google’s INP and which page speeds will need improvement.
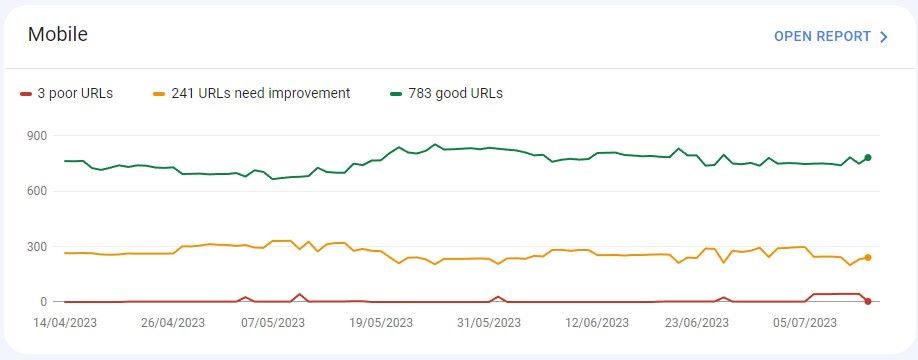
To identify how to improve different page speeds, run several different types of content through the Web Dev Page Speed Test. Review results for both desktop and mobile devices.
7. Images
The above web speed testing tool will identify whether images are too large and may make recommendations for specific CMS systems.
It also helps to put ALT tags on large images that help identify what an image is. Best SEO practice for ALT tags is to:
- Use descriptive and relevant keywords in ALT tags.
- Write unique ALT tags for each image, avoiding duplicate content.
- Don’t overstuff ALT tags with keywords.
- Ensure they accurately describe the image’s content and purpose.
- For optimal SEO, ALT tags should be similar to the file name.
If image searches are important for your site, then ALT tags should be one of your priorities. On the other hand, they have relatively little impact on where your site will rank in the main organic search results, though they are important for website accessibility.
8. XML sitemap
An XML Sitemap tells Google how frequently different pages are updated and lists all the URLs you want indexed. It speeds up indexing and re-indexing of pages that regularly have new content.
Most CMS systems have an automatically generated XML Sitemap which is simpler to use than having to code one.
Depending on your CMS, install the following free plugin/module:
- WordPress – XML Sitemap Generator for Google plugin
- Drupal – XML Sitemap module
For other CMS systems see how to create an XML Sitemap for SEO.
9. URL structure
Google’s Search Guidelines advise webmasters to:
“Keep a simple URL structure. Consider organising your content so that URLs are constructed logically and in a manner that is most intelligible to humans. When possible, use readable words rather than long ID numbers in your URLs.”
Ensure that your URL structure fits this description. Enterprise websites often use more sub-folders than smaller sites. If in doubt, review top-ranking competitors to identify the URL structures they use. If your corporation uses more complex URL structures, simplify it. For landing pages, check whether each URL includes a keyword.
For multilingual sites, check that the URL is localised for each language. Ensure that old URLs are 301 redirected to new ones.
SEO content audit
Meta Titles and Descriptions appear in Google’s search results and are one of the most important elements of on-page SEO.
- Meta titles should be 60 characters or less and include an important keyword. It’s also important that they read well and are not just a string of keywords.
- Meta descriptions should be 120-160 characters long, include keywords or close-variants of them and entice searchers to visit your site.
For enterprise SEO audits, it’s important to not just look at individual pages, but also review the default Meta Titles and Descriptions. Ask yourself if it’s possible to edit the default settings per content type to make more Meta Tags fit the above character length, include keywords, or simply read better. In major CMS platforms like WordPress or Drupal, you can enter custom variables into the Meta Titles, which helps optimise different sections.
As well as refining your default Meta Tags, it’s also worth manually reviewing your priority landing pages using the above guidelines.
Screaming Frog is the best SEO tool for this. Follow the steps below:
- Open Screaming Frog
- Go to Configuration / API Access/ Google Analytics 4 and connect to your GA4 account.
- Repeat for Google Search Console
- Filter by HTML only
- View and export the Page titles
- View and export the Meta descriptions
The diagram below shows where the different buttons are located to complete all the above steps.
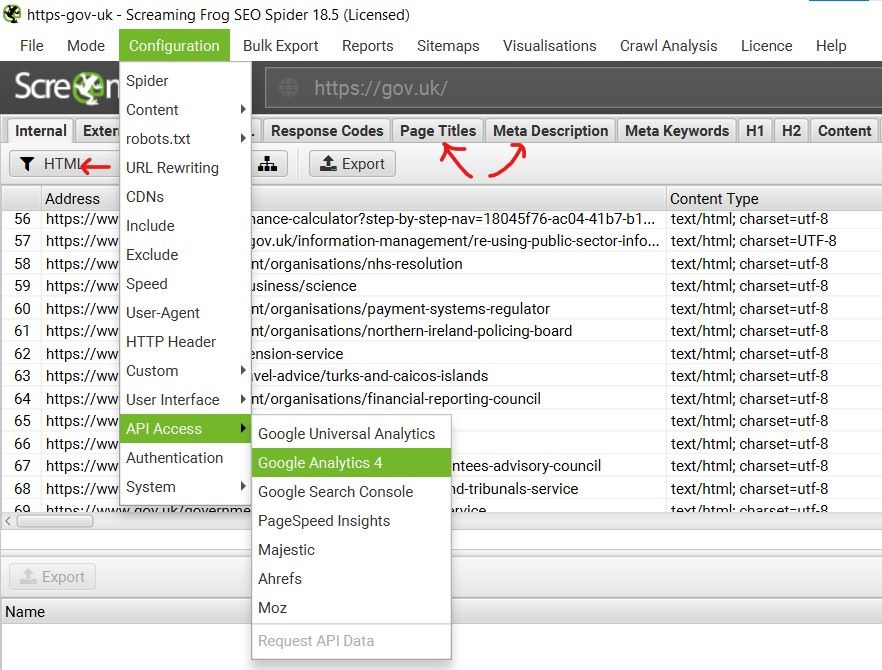
Connecting Google Analytics 4 and Search Console adds extra columns to Screaming Frog’s full SEO report. This allows you to view Clicks, Sessions, Views and Conversions. Including these in SEO reports means you can easily sort by one or more of the website statistics, making it considerably easier to prioritise important pages.
Decide how many pages to optimise the Meta Tags for and rewrite the Meta Titles and Descriptions as necessary. For corporate SEO audits, 100 pages is a good starting point.
12. H1 headings
H1 headings are the main visible heading of a web page. Each page should have only one H1 heading which summarises what the page is about. To extract H1 headings, use Screaming Frog and click the H1 tab.
Many SEO consultants recommend including a keyword in every H1 heading. Enterprises, however, are often reluctant to do so, as it can negatively impact page design. For example, using the word, “Service” as part of every single heading might be off-putting.
H1’s are less of a ranking factor than Meta Titles and you have more freedom over both keyword usage and length. We therefore recommend ensuring that:
- Every page has one and only one H1.
- Landing pages include a keyword or component of a keyword. For example, if your keyword is “Finance and Banking Services”, using “Finance and Banking” is absolutely fine.
13. H2-H6 Headings
To review subheadings of an entire enterprise site, identify the subheading structure in the following fashion:
- Identify all the different content types your site has. For example, this might include the home page, category listing, service page, and blog page.
- Visit a typical URL from each content type in Chrome.
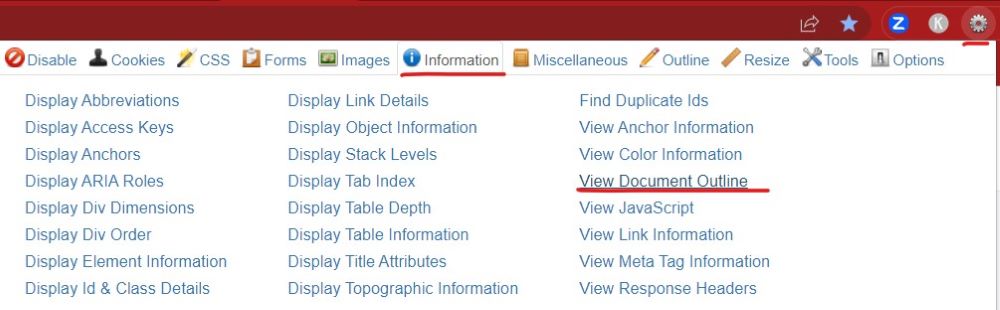
- For each content type, click the Web Developer cog icon.
- Go to the Information tab, then choose View Document Outline.
- For each content type, review the headings and see if there are any missing (e.g. where you have a H1 heading, then a H4 heading immediately after it, but with no H2 or H3 headings in-between).
- Identify whether there are any common site components that shouldn’t be included. Common examples are buttons, footer menu headings, or long passages of text.
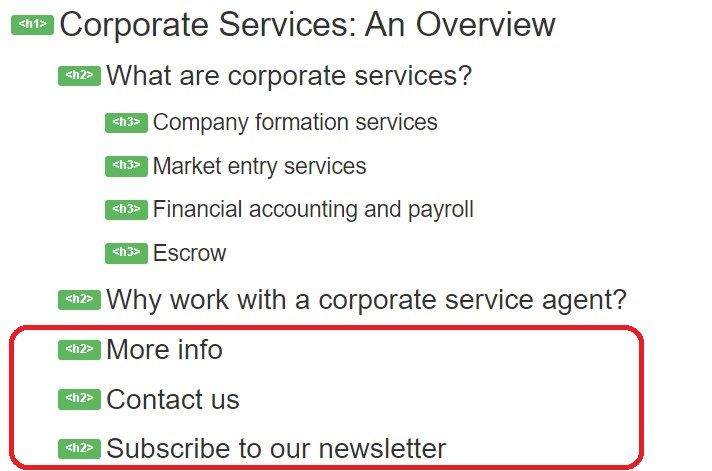
In the example below, the last 3 headings aren’t really headings. They’re actually buttons or calls to action and would be better as <p> text, then configured using CSS to look however you want them to look.
14. Bounce rates
In Google Analytics 4, bounce rates are measured as visits that:
- Lasted less than 10 seconds.
- Did not contain a conversion event (when a user completes an activity that is important to your business).
- Only viewed a single web page on your site.
This is the opposite of ‘Engaged Sessions’. When running your enterprise website audit, review pages that have a high bounce rate in order to identify common elements between them. Compare these pages to those with a high engagement rate and outline what the difference is. This provides an excellent SEO strategy to optimise your site. Learn more about GA4 bounce rate and engaged sessions.
15. Duplicate content
Where you have two pages with very similar content, this causes SEO issues as Google doesn’t know which one to show and the benefit of incoming links is split between them.
Professional SEO tools like Ahrefs and Semrush include duplicate content checkers as part of their service. If you’re looking for a free duplicate content tool that can check the whole site, your best bet is to look for duplicate Meta Titles or Meta Descriptions using Screaming Frog.
To do so:
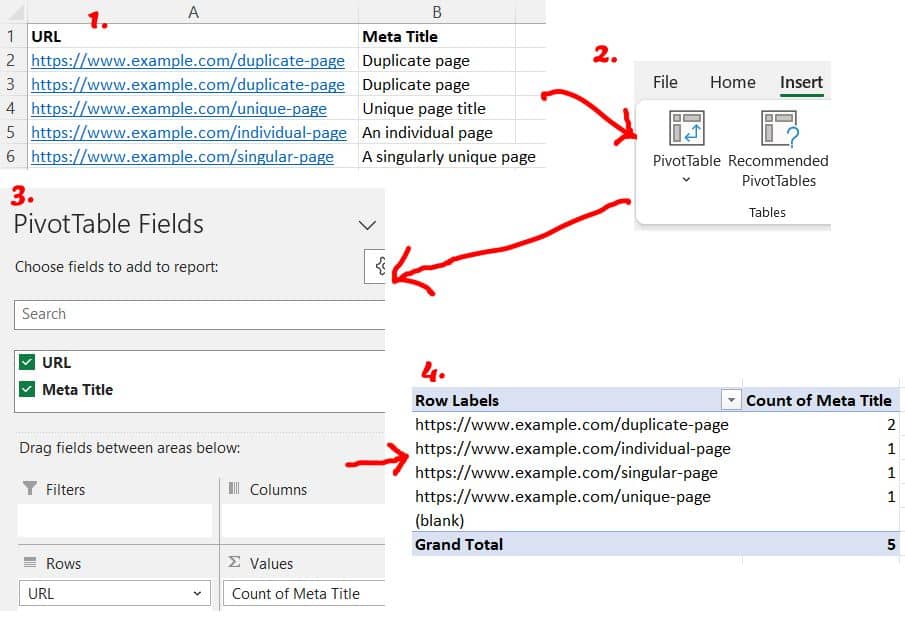
- Run the Screaming Frog Meta Title report, then export it and open it in Excel.
- Open a new tab, then go to the Insert menu and choose PivotTable.
- Highlight the data you just entered, then drag the ‘URL’ field to Rows and the ‘Meta Title’ field to Values.
- It will now show you a list of URLs with a count of how many times each Meta Title appears. Sort by ‘Count of Meta Title’. Any value over 1 indicates there’s a duplicate title.
16. Content needing a refresh
Some content ranks well at first but becomes outdated and has a decline in traffic. In order to identify content this has happened to, open Google Search Console and:
- Go to Search Results
- Click Date, then click the Compare tab at the top of the window.
- Choose suitable comparison dates (e.g. “Last 3 months to previous period”).
- Scroll down and press Pages
- Choose “Clicks Difference” twice.
This will then show the pages that have lost the most organic clicks over the last 3 months. Consider whether this is due to content needing a refresh, or some other factor (e.g. a seasonal change).
It’s particularly important to complete this aspect of a content audit 3 months after a website redesign or other major site change. This identifies pages that have suffered as a result of the redesign and implies the previous layout worked better for these pages.
Moreover, supplementing this process with the creation of a content style guide can ensure consistent messaging and branding throughout all digital platforms.
17. Menus
Your most important service landing pages will rank higher if they are included in your main menu. Similarly, your menu shouldn’t be cluttered with pages that clients never visit. This reduces the link juice going to your priority pages.
- Open a page with very few links out of it, other than the main menus.
- Click the Web Developer icon in Chrome.
- Click the Information tab.
- Click View Link Information.
Review the links and check whether your priority pages are in there.
Other enterprise SEO factors
18. Conversion rate optimisation
Let’s say you have identified increasing sales or enquiries as one of your KPIs. There are fours ways to do it:
- Increase organic traffic through a mixture of on-page SEO and link building.
- Increase paid traffic by expanding or improving your advertising.
- Increase your conversion rate by improving your UX.
- A mixture of the above.
Of these, your conversion rate is the factor we would recommend starting with. This is because small changes can drive dramatic results. An improved conversion rate will:
- Improve your SEO. This is because improved conversions lower your bounce rate and increase time on site, two factors Google values when deciding where to position your website.
- Increase your ROI from advertising.
- Generate more sales or enquiries by itself.
Conversion rate optimisation involves analysing numerous interconnected factors that influence conversions. Discover our conversion rate optimisation service for assistance with applying different strategies, measuring the results, and completing A/B tests to increase conversions.
19. Manual web design audit
It’s important to complete your audit using a combination of SEO tools and manual techniques. Ask yourself if the website is easily accessible, logical and professional. For example:
- Is text difficult to read due to it being too small, or having little contrast between the background and foreground colour? Check on both mobiles and desktops.
- Is there plenty of white space separating different sections?
- Are links to your contact page clearly visible?
- Does your contact form have unneccessary fields, or it cluttered in any way?
- Do images immediately convey a sense of the services being offered? Can you read any text on images when on a mobile device?
- Do any other aspects of the site need redesigning? If so, how?
20. Audit and disavow toxic backlinks
Do you have a lot of spammy backlinks going to your site?
Search Console allows you to do free backlink monitoring, but doesn’t specify whether links are “toxic”. If you’re concerned, you may wish to use a backlink audit tool like Semrush or Ahrefs to review your backlink profile, identify toxic backlinks, and disavow them.
Warning – Google specifies that:
“This is an advanced feature and should only be used with caution. If used incorrectly, this feature can potentially harm your site’s performance in Google Search results.”
For the majority of sites, it’s not necessary to disavow any backlinks. If you’re concerned, we recommend using one of the above tools and checking each backlink to ensure that it doesn’t offer any value. Only disavow backlinks that you are certain are spammy, you are far better off missing several spam links than you are inadvertently disavowing good quality links.
If your link building audit reveals a large number of toxic backlinks, then it indicates you need to modify your link building strategy. Consider switching to a manual link building service that includes editorial outreach. Avoid placing links on long lists of sites in a private blog network.
21. Enterprise SEO strategy
Your Enterprise SEO Audit should identify:
- Your KPIs.
- Quick-wins in the form of actions your site needs to rapidly improve its SEO.
- Longer-term SEO strategy based on your website analysis.
Depending on your findings, your longer-term strategy might include elements such as:
- Ongoing content creation and on-page SEO.
- Prioritising the more complex technical SEO elements.
- Creating a backlink strategy through the use of editorial content.
- Other actions to improve your SEO over an extended period.
If you would like us to complete an SEO Audit for you, or need the help of a dedicated team of SEO consultants, don’t hesitate to request a free consultation.
- How to Blend GA4 & UA Data Using BigQuery & Looker Studio - 12/07/2024
- How to do a Google Analytics 4 Audit & Mistakes to Avoid - 10/07/2024
- How to Backup & Visualize GA3 Data for Free - 27/06/2024
An insightful guide to enterprise SEO audit! This blog breaks down the complexities of auditing large-scale websites and offers practical tips for optimizing their performance. A valuable resource for businesses looking to enhance their online presence and drive organic growth.